Managing Cron Jobs in cPanel
Cron Jobs allow you to automate recurring tasks on your server, such as backups, email sending, cache cleaning, or updating data. They're especially useful for maintaining websites or running scheduled scripts without manual intervention.
How to Add or Edit a Cron Job
- Log in to your cPanel account.
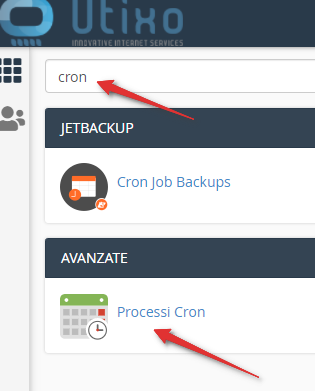
- Use the search bar at the top and type "cron", then click on Cron Jobs.
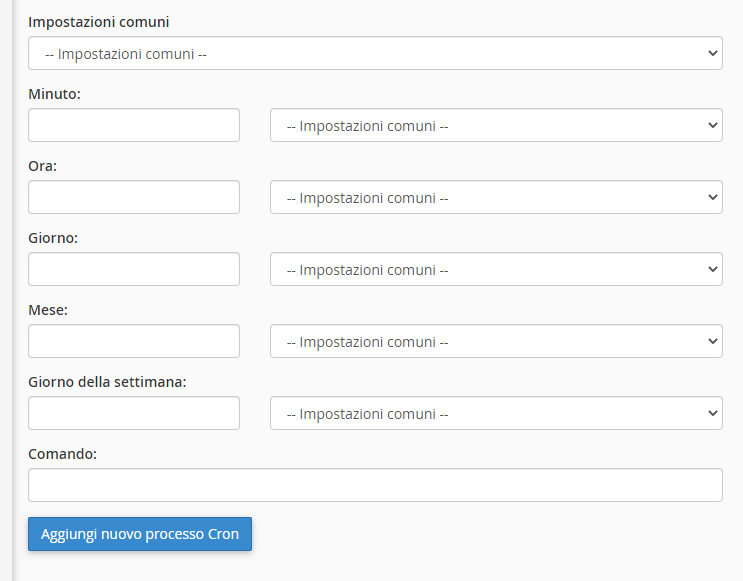
- In the Add New Cron Job section, set the desired time/frequency and enter the command you want to run.
Examples of Cron Commands
- Run a PHP script every hour:
/usr/local/bin/php /home/youruser/public_html/script.php - Call a URL (wget) daily:
wget -q -O - https://www.yourdomain.com/script.php > /dev/null 2>&1 - Run a task every Monday at 3:00 AM:
Set the time field to:0 3 * * 1
Understanding Cron Time Syntax
Each Cron Job has 5 time fields:
* * * * * command │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └─ Day of the week (0-7) │ │ │ └─── Month (1-12) │ │ └───── Day of the month (1-31) │ └─────── Hour (0-23) └───────── Minute (0-59)
Tips
- Avoid running cron jobs too frequently, especially on shared hosting plans.
- Add logging or notifications to ensure your script executes as expected.
- If you'd like to receive email output, set your address in the Cron Email field at the top of the page.
Cron Email Notifications (Optional)
You can receive execution reports via email by filling in the Email field. If you prefer not to receive them, append the following to the end of your command:
> /dev/null 2>&1

